The Mathematics Behind Artificial Intelligence
-
Engineer Duru
-
 AI, Maths, Science
AI, Maths, Science
-
 0 comment
0 comment
-
 29 Nov, 2025
29 Nov, 2025
Artificial Intelligence (AI) often feels like magic. Machines recognize faces, translate languages, and even write poetry. But beneath the surface, AI is powered by something far more fundamental: mathematics. In this post, we’ll explore the three pillars of math that make AI possible—linear algebra, probability & statistics, and calculus & optimization—and even look at a Python simulation that brings these ideas to life.
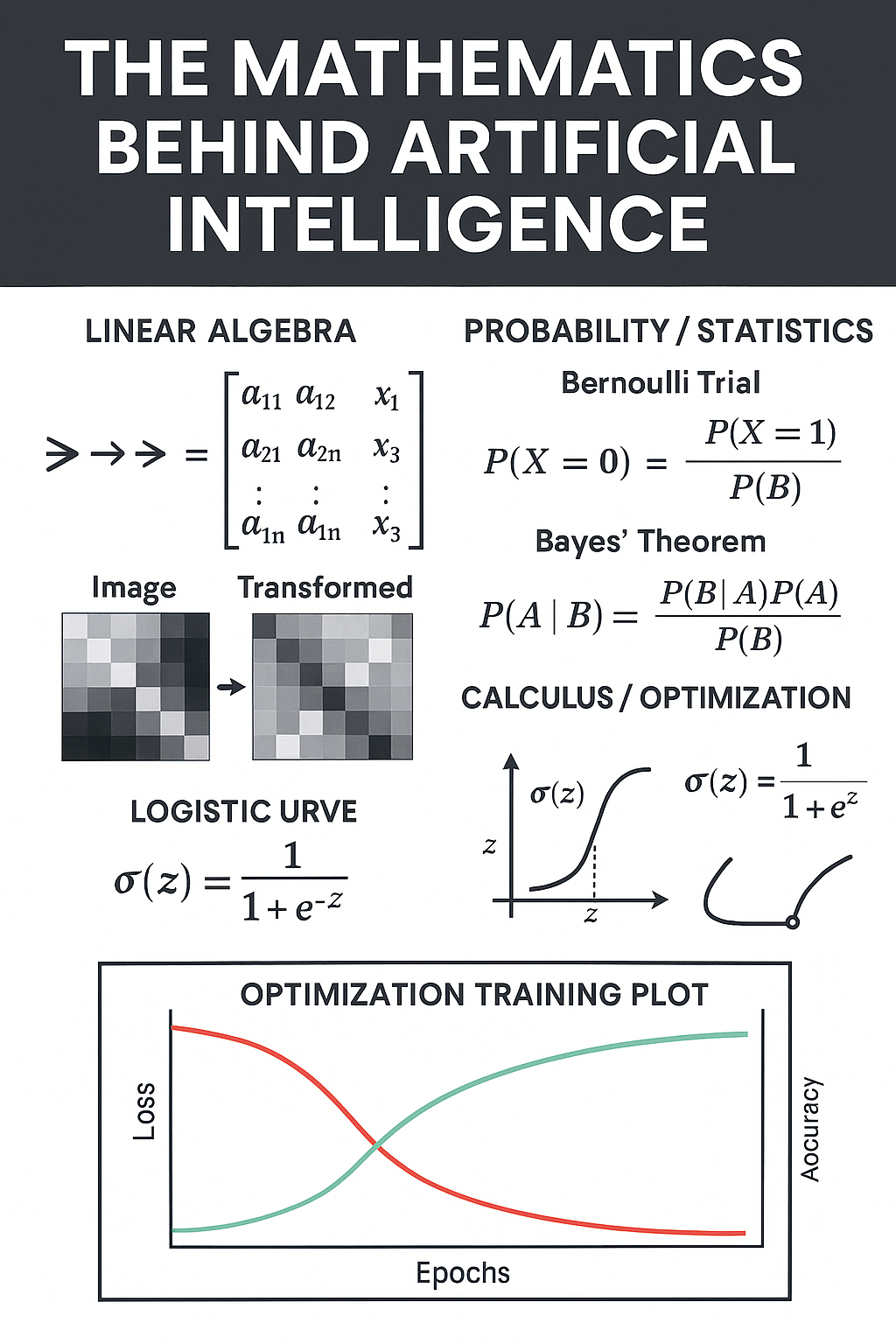
Linear Algebra: Moving Data
At its core, AI is about numbers. Images, sounds, and words can all be represented as vectors and matrices—grids of numbers that capture information.
Matrix multiplication transforms data: rotate an image, compress a sound, or shift meaning in language.
Neural networks rely on these transformations to pass information forward, layer by layer.
Think of linear algebra as the engine that moves data through the AI pipeline.
Probability & Statistics: Guiding Decisions
AI doesn’t just move data—it makes decisions under uncertainty.
Probability distributions answer questions like: “What’s the chance this email is spam?”
Statistics help AI learn patterns from data, turning raw numbers into predictions.
Bayes’ theorem and logistic functions are the mathematical tools that allow AI to weigh evidence and update beliefs.
Probability is the compass that guides AI toward the most likely outcome.
Calculus & Optimization: Teaching Learning
AI learns by minimizing error. This is where calculus comes in.
Gradient descent is the process of rolling downhill toward the lowest error.
Each step adjusts the model’s weights, making predictions more accurate.
Over time, loss decreases while accuracy rises—a clear sign of learning.
Calculus is the teacher, showing AI how to improve with each iteration.
A Python Simulation of AI Math
To make this concrete, here’s a quick overview of a Python simulation built with SimPy and Matplotlib:
Producer: Generates synthetic data batches.
Linear Algebra Transform: Applies matrix operations to reshape data.
Probability Classification: Estimates outcomes with logistic scoring.
Trainer: Uses gradient descent to minimize error.
Plots: At the end, Matplotlib shows Loss vs Time and Accuracy vs Time.
The result? A mini AI factory where you can watch math in action—loss curves falling, accuracy curves rising.
Faith + Tech Reflection
Just as Proverbs reminds us, “By wisdom a house is built” (Proverbs 24:3). AI, too, is built on unseen foundations—mathematics. Whether in faith or technology, the invisible structures are what make everything else possible.
Conclusion
AI isn’t magic—it’s math.
Linear algebra moves data.
Probability guides decisions.
Calculus teaches learning.
If you want to understand AI, start with the math. It’s the true code of intelligence.
Engineer Duru
0 comment